Endometriosis
Endometriosis
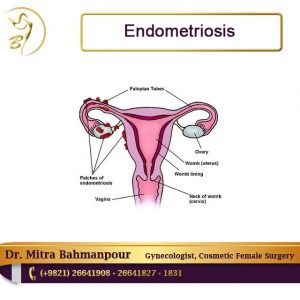
Endometriosis is a painful disorder in women that tissues that are inside the uterus, the endometrium, grows outside the uterus. Pelvis is the most common place for endometriosis. In this condition, endometrium displaced and continues to its normal activity, and becomes thicken and bleeds in each menstrual cycle.
During endometriosis, surrounding tissues may become stimulated and then result in damaging and adhesions. Women may have severe pain during their menstrual cycle.
What are the symptoms of endometriosis?
- Pelvic pain
The first symptom of endometriosis is pelvic pain which can be associated with menstrual period. Women may experienced menstrual cramps. This symptoms often begins before the period.
- Painful periods (dysmenorrhea)
- Pain during or after sexual intercourse
- Pain during urination
- Infertility
- Fatigue, diarrhea, constipation or bloat are other symptoms of endometriosis
The severity of pain varies from one woman to the other one, that ranges between mild to severe, some women have no pain. Endometriosis can be mistaken with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) that causes diarrhea, constipation and abdomen pain.
Endometriosis causes
5 common causes if this condition is considered:
- Retrograde menstruation
Blood consists of endometrial cells flow back to the pelvic cavity through the fallopian tube. These cells stick to the endometrial cells and grow there and result in bleeding.
- Embryonic cell growth
These cells cover the pelvic and abdominal cavities. When these cells change into the endometrium, then, endometriosis will occur.
- Surgery
After surgeries such as hysterectomy or caesarean section, can attach to the surgical incisions and scars.
- Immune system disorder
Any disorder in immune system can destroy endometrial tissues and growing them outside the uterus.
What are the risk factor of endometriosis?
Some of the following factors can increase the risk of endometriosis:
- No pregnancy
- Family background
- Pelvic infection background
- Uterine disorders
Signs of the endometriosis fade after the pregnancy or menopause, if to take estrogen.
How to diagnose endometriosis?
- Pelvic examination by the gynecologist to consider existence of the cysts or uterus scars.
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Laparoscopy to determine location and size of the endometrium.
Endometriosis treatment
- Using calmatives
- Hormonal treatment to reduce the pain of endometriosis. Changing the hormones results in thickness of the endometrium and bleeding.
- Surgery
- In severe cases, surgery should done to remove the uterus and ovaries.
Dr. Mitra Bahmanpour, Gynecologist:
Address: Khalij Fars Building. Next to 18th st. Velenjak. Tehran. Iran
Tell: +9821- 26641827
+9821- 26641908
+9821- 1831
+98912- 0897425